MBR and GUID Partition Table-How to Use Hard Drive (IV)
Partition table is the most basic concept of using hard drive, and you might have heard about MBR and GUID which mean partition table.
What is partition? Partition is the operation of dividing hard drive into several separated areas for better use of hard drive space. There is usually one physical hard drive on computer, but there is not only one C partition on the drive, you might have D, E, F partitions. It is partitioning that divides one hard drive into C, D, E, and F partitions.
There are currently two types of partition table: MBR and GUID. MBR is traditional partition table style which is not able to better manage hard drive whose capacity exceeds 2TB; GUID is new partition table format, which has many advantages over MBR, especially in managing large hard drives.
For the moment, the number of hard drive using MBR is far more than hard drive with GPT partition table. But as far as development trend concerned, GPT will gain more popularity.
MBR Partition Table
The structure of MBR partition table is not so complicated, and yet this articles doesn't talk about technology details about. This article mainly dedicates to how to use MBR partition and some problems that worth our attentions.
Partitions using MBR partition table are classified into primary partition, extended partition and logical partition.
Primary partition: primary partition can be created on hard drive and used to store or access data directly.
Extended partition: extended can be created on hard drive directly, but it can't be used to store or access data until logical partitions are created on it.
Logical partition: logical can't be created directly from hard drive, as it can only be created on extended partition.
You might have heard about active partition that usually installs operating system. There is only one active partition on hard drive and only primary partition can be set as active partition. In most cases, the active partition is C partition.
MBR partition table has some limitations which restrict its performance and give rise to bad management of large hard drive.
1. There are no more than four primary partitions, which means hard drive can be partitioned to 4 primary partitions at most.
2. A hard drive can have one extended partition at most. Since extended partition can be regarded as a special primary partition, so the total number of primary partition and extended partition is up to four. Therefore, a hard drive can contain three primary partitions and one extended partition at the most.
3. There is no limitation on the number of logical partition. As a matter of fact, the purpose that Microsoft introduces the concept of extended partition and logical partition is breaking the restriction that MBR partition table allows up to four primary partitions.
4. Any partition, including partition, logical partition or extended partition can't be larger than 2TB. This is the very restriction that MBR partition table can't manage large hard drive.
5. No partition is allowed to start after the physical location of 2TB. Actually, not only starting location, but also the ending location can't exceed the 2TB physical location, otherwise, sever problem may happen to hard drive. This limitation declares that MBR partition table is not appropriate for the management hard drive whose capacity is large than 2TB.
6. UEFI is the new generation of BIOS. Nowadays, brand new computers and laptops start to support UEFI. This article is not going to explain what UEFI is, but you can search for related materials online. UEFI usually comes with GPT partition table.
If the capacity of your hard drive is within 2TB, you can have no worries to use MBR partition table, which is easy-to-use, reliable and efficient. Furthermore, MBR has great compatibility with all Windows system, including Windows XP/vista/7/8, 32bit and 64 bit.
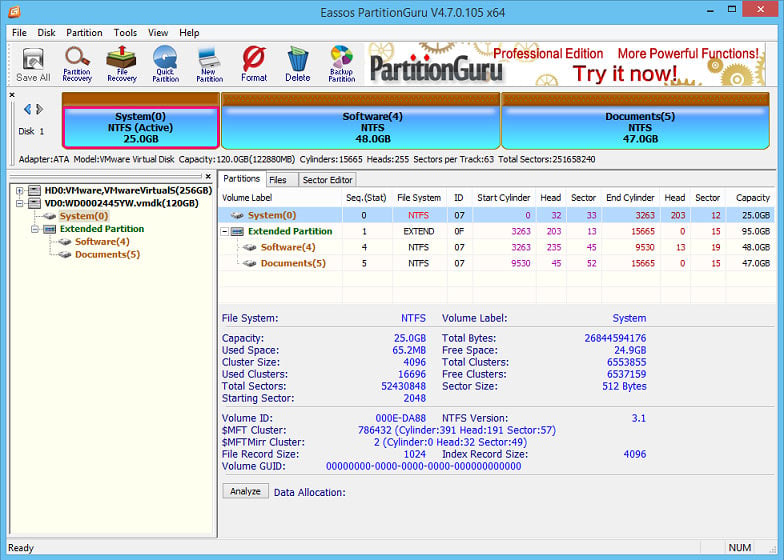
In general, hard drive with MBR partition is divided into one primary partition and one extended partition. Several logical partitions can be further divided on extended partition if necessary. The following picture shows the hard drive and partitions details of my computer via free partition manager DiskGenius.
GPT Partition Table
If your hard drive has a capacity of more than 2TB or your computer is UEFI-based machine, then GPT partition table can meet your requirements better. GPT partition table is new partition table style which cooperates with UEFI and manages large hard disk well.
Technology details of GPT partition table which is actually much more complicated than MBR and that won't be discussed here either. But, this tutorial covers basic knowledge of using GPT partition table.
1. GPT no longer uses those concepts like extended partition and logical partition which are used by MBR partition table.
2. A hard drive with GPT partition can be divided into as many as 128 partitions under Windows, which is quite enough already.
3. One single partition from GPT partition table can be as large as 18EB (1EB=1024PB=1,048,576TB), so there is no need to consider hard drive capacity anymore.
4. GPT is good partner of UEFI-based computer, but it is not highly advised to use GPT on old bios machines in case of unexpected problems.
5. GPT partition table is well compatible with Windows, including Windows 7/8/10 and 64-bit XP.
So much for the notes about GPT. The obvious merit of GPT partition is the support of large hard drive. UEFI is the updating and alternative of old bios. For more info about UEFI, you can search online and learn by yourself.
GPT is still not well mastered by some users, so they may deem that it is a little bit complex to install system on GPT disk.
Advice: it is suggested that old computers with old bios choose MBR partition table, and UEFI-based computer use GPT. It is not wise if you use them in turn, for problem may happen.
Sometimes, we need to convert MBR partition table to GPT or convert GPT to MBR, and DiskGenius can do the conversion for free without data loss.
Hard Drive Without Partition Table
In fact, USB flash drive, SD card, Micro SD card and other removable disks can be regarded as a special type of hard drive. These removable drives do not have partition table, but they still can be recognized by operating system and treated as one partition. Actually, partition table is not very useful for removable disks, because Windows only can recognize the first partition on removable drive, even though it has been divided into two or more partitions.
External hard drive is different from USB flash drive in that it can be recognized as one partition by system if it doesn't have a partition table; besides, external hard drive can be divided into two or more partitions and all partitions can be recognized by operating system, which is the same as internal hard drive.
This tutorial of MBR and GPT will end here, and next chapter will refers to file system.














 Facebook
Facebook X
X Youtube
Youtube